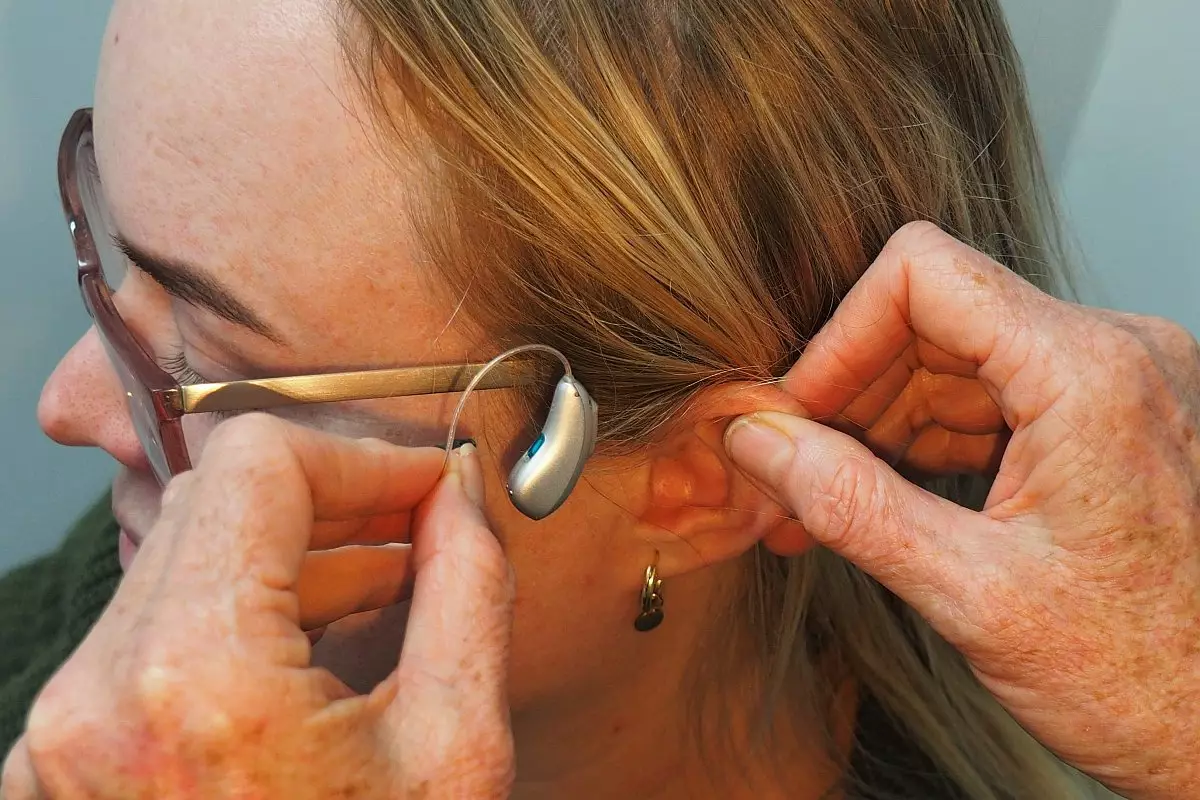
In a significant step toward improving accessibility for individuals with hearing impairments, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has announced new regulations that require all mobile phones sold in the United States to be compatible with hearing aids. This landmark decision is set to benefit approximately 48 million Americans who experience hearing loss, making it essential for mobile device manufacturers to prioritize inclusivity in their product designs.
Over the years, the FCC has recognized the challenges faced by individuals with hearing difficulties, particularly when it comes to mobile communications. With the increasing reliance on smartphones in everyday life, ensuring that these devices can be used effectively by people with hearing impairments is paramount. The newly adopted rules underline the FCC’s commitment to fostering an inclusive digital environment where technology is accessible to everyone, regardless of their auditory capabilities.
The FCC’s initiative has been informed by collaboration with the Hearing Aid Compatibility (HAC) Task Force. This group, which includes representatives from smartphone manufacturers, research organizations, service providers, and individuals with hearing impairments, has paved the way for establishing viable standards for compatibility. By conducting in-depth research and engaging with stakeholders, the Task Force has highlighted the urgent need for comprehensive regulations that reflect the realities of today’s mobile technology landscape.
Under the new rules, manufacturers are mandated to ensure that 100 percent of their new mobile handsets are compatible with hearing aids. This is a significant leap from the previous requirement, where only 85 percent of models needed to meet these standards. Importantly, the FCC has also included cochlear implants within the definition of hearing aids, ensuring a broader scope of accessibility.
Furthermore, the FCC has introduced new Bluetooth coupling requirements, which aim to standardize connectivity between smartphones and hearing aids. This move seeks to eliminate the use of proprietary connection standards that can hinder usability and create barriers for consumers. By fostering universal connectivity, the FCC is not only enhancing the user experience for hearing aid wearers but is also promoting a more cohesive technology ecosystem.
As part of this initiative, manufacturers will also be required to provide detailed product information. This includes indications of compatibility with hearing aids and compliance with the newly introduced volume control benchmarks—an essential aspect that ensures users can increase volume levels without distortion.
While these new regulations are indeed a major step forward, the FCC has yet to specify a timeline for compliance. The transition period has been acknowledged, but without clear deadlines, it raises questions about how swiftly manufacturers will adapt to these requirements. Industry observers will undoubtedly be watching closely to see how quickly companies plan to implement these standards and whether additional support will be provided to facilitate this transition.
Many prominent manufacturers have already made strides in meeting the previous regulations. For instance, Apple has ensured that all its smartphones, starting from the iPhone 6 series to the latest iPhone 16, are compatible with hearing aids. Similarly, Google’s Pixel smartphones and a significant number of Samsung’s Galaxy series have also adhered to existing standards. This proactive approach reflects a growing acknowledgment within the tech industry of the need for accessible designs.
However, the introduction of the 100 percent compliance requirement signifies a more rigorous expectation for all manufacturers, particularly smaller companies that may lack the resources to facilitate these changes promptly. It will be crucial for these manufacturers to engage with the rules early on and consider innovative solutions for making their products accessible.
The implications of the FCC’s new regulations extend beyond simple compliance; they represent a fundamental shift in how technology integrates into our daily lives. By prioritizing accessibility, the FCC is championing a more inclusive society where technological advancements can be enjoyed by all. This initiative holds the potential not just to improve individual experiences but to create a paradigm that values and prioritizes inclusivity at its core.
As the landscape of mobile technology continues to evolve, ongoing dialogue between regulators, manufacturers, and consumers will be essential in ensuring that the needs of individuals with hearing impairments are consistently met, paving the way for future innovations that embrace accessibility as a fundamental principle.

Leave a Reply